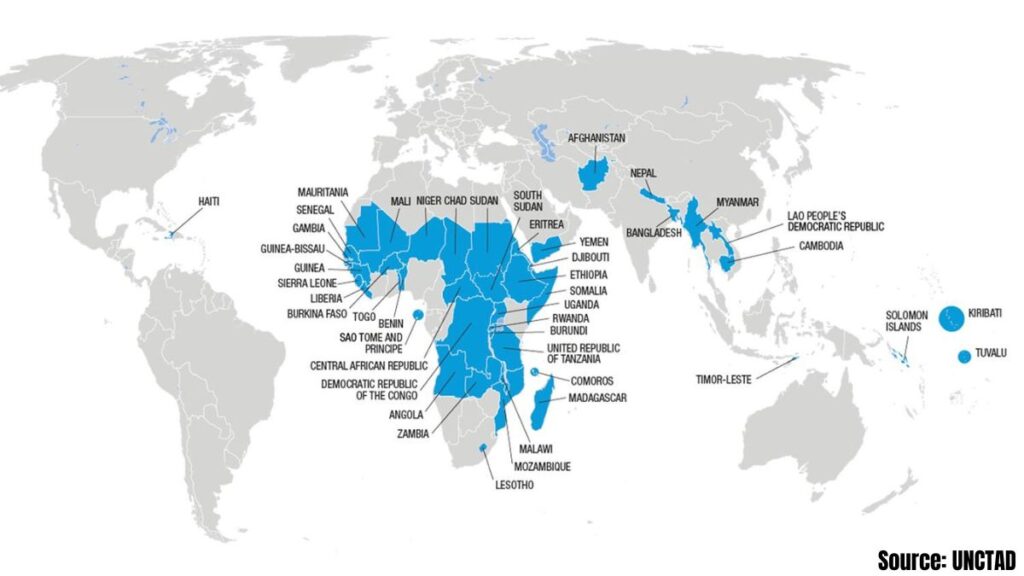
By 2025, the list of Third World Countries includes 45 countries across Africa, Asia, the Caribbean and the Pacific, facing development challenges. The term “Third World” is now often replaced by more precise expressions such as “developing countries”. Criteria for inclusion include income levels, human assets, and economic and environmental vulnerability indicators. This list is reviewed by the United Nations every three years, ensuring continued accuracy and relevance.
During the Cold War, the moniker ‘Third World’ emerged to delineate countries not affiliated with the Western Bloc (NATO) or the Eastern bloc, the Communist bloc. Today, the term often characterizes countries going through stages of development in Africa, Asia, the Caribbean and the Pacific.
Over time, the term has acquired a flexible semantic scope. In this presentation, ‘Third World’ will be used to refer to countries that are experiencing shortcomings, underdevelopment or lackluster performance in specific areas, warranting urgent attention for their development.
Third World Countries 2025
Contemporary speakers and writers often avoid using the term ‘Third World’ in favor of more precise and measured expressions such as ‘developing countries’ and ‘least developed countries’ , as defined by the United Nations Human Development Index, or ‘low-income countries’,’ according to World Bank data.
The 45 countries classified by UNCTAD as least developed countries are classified according to four regions. Below is the full list of third countries:
Related stories
| Continent | Country number | Nation |
| Africa | 33 | Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Democratic Republic of Congo, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia |
| Asia | 8 | Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Nepal, Timor-Leste, Yemen |
| Caribbean region | 1 | Haiti |
| Pacific | 3 | Kiribati, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu |
Monaco, Nauru, North Korea and Somalia, all United Nations member states, are typically excluded from the Human Development Index. Including these countries would likely result in all but Monaco being classified as developing or least developed countries.
The list presented here is taken from the United Nations list of least developed countries and is not arranged in any particular order. Currently, there are 45 economies recognized by the United Nations as least developed countries (LDCs). This designation gives them access to preferential market opportunities, aid, specialized technical assistance and technological capacity building, among other concessions.
The list of LDCs is comprehensively evaluated every three years by the Commission for Development Policy (CDP), an independent group of experts that reports to the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the United Nations. After the triennial review, the CDP may propose, in its report to ECOSOC, the addition of countries to the list or the removal of their LDC status. The upcoming triennial review is scheduled for March 2025 and appropriate data will be updated promptly as they become available.
ALSO READ| List of 7 countries with the highest GDP in 2023
Criteria for inclusion in LDC
Income criteria:
- Threshold Includes $1,088 or less
- The Graduation Threshold is $1,306 or more
- Measurement: Three-year average estimate of Gross National Income (GNI) per capita in US dollars.
Human Asset Index (HAI):
Health sub-index:
- Indicators: Mortality rate in children under 5 years old Maternal mortality rate Stunting rate
- Inclusion and Graduation Thresholds: 60 or less and 66 or more, respectively.
Education sub-index:
- Indicator: Lower secondary school completion rate Adult literacy rate Gender equality index at lower secondary school completion
- Inclusion and Graduation Thresholds: 60 or less and 66 or more, respectively.
ALSO CHECK | Countries with the best education in 2023: According to the Global Education Partnership
Economic and Environmental Vulnerability Index (EVI):
Economic vulnerability sub-index:
- Index: Share of agriculture, forestry and fishing in GDP Remote and landlocked regions Concentration of commodity exports Volatility of exports of goods and services
- Inclusion and Graduation Thresholds: 36 and above and 32 and below, respectively.
Environmental vulnerability sub-index:
- Indicator: Percentage of population in coastal areas with low altitudes Percentage of population living in arid lands Unstable agricultural production Victims of natural disasters
- Inclusion and Graduation Thresholds: 36 and above and 32 and below, respectively.
General Note: All indices are constructed using established methods with equal weighting of the indices included.
ALSO READ| How many countries are there in the world?
ALSO READ| List of countries and their currencies